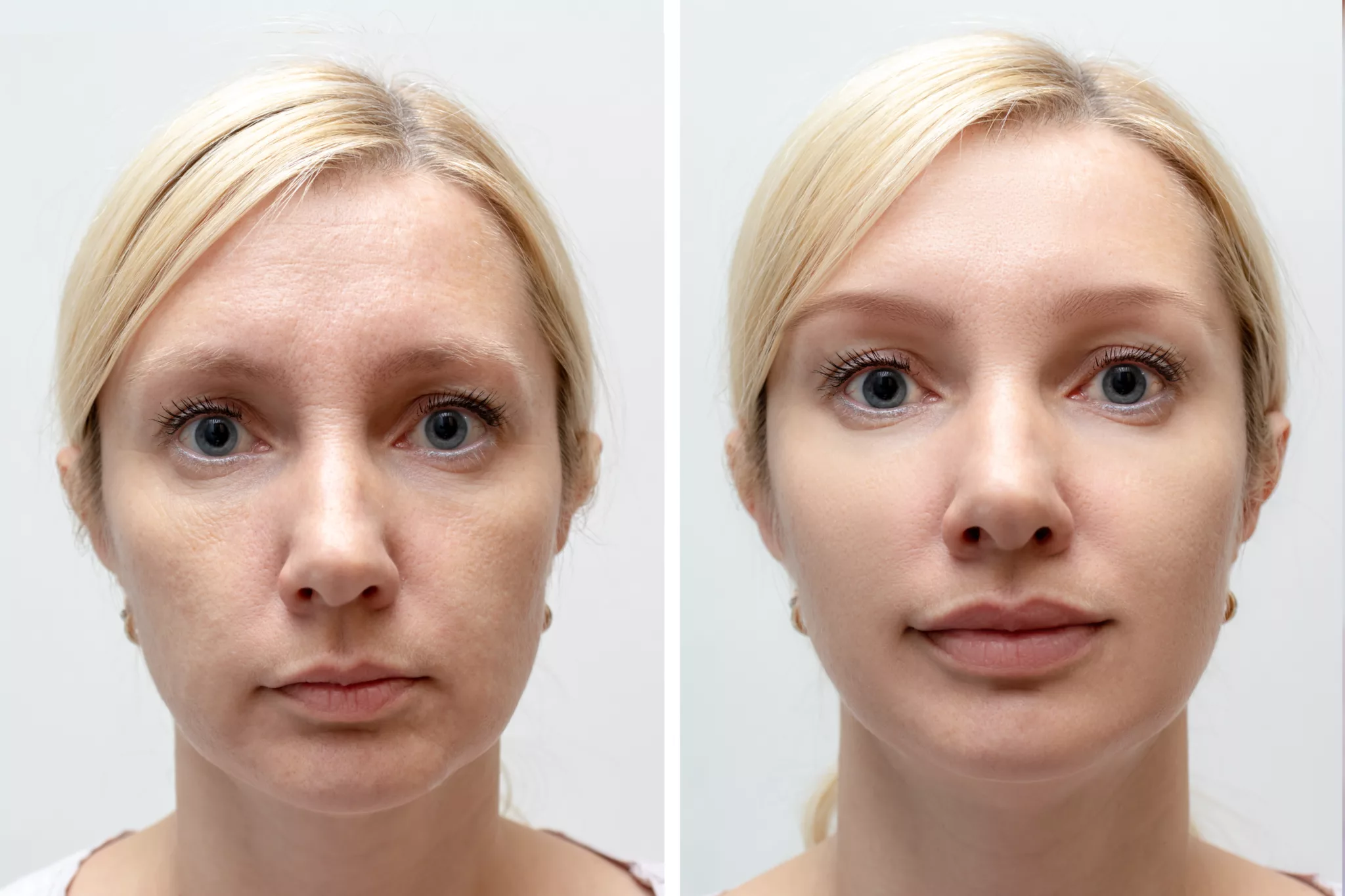
Botox blocks neurotransmitters that trigger forehead muscle movements, reducing dynamic wrinkles. Visible smoothing starts in 3–7 days, with full effects at two weeks. The frontalis muscle, responsible for horizontal lines, relaxes temporarily. Results diminish as nerve endings regenerate over 3–6 months.
Over-Treatment Leads to ‘Frozen’ Expressions and Eyebrow Drop
Excessive doses paralyze muscles beyond wrinkle reduction, limiting natural facial movements. Drooping eyebrows occur if toxin spreads to lift-related muscles. Skilled injectors use 2–4 units per site to preserve subtlety. Customized dosing accounts for muscle strength and patient age.
Men’s Thicker Forehead Muscles Demand Higher Botox Doses
Male patients often require 25–50 units versus 15–30 for women. Denser muscle fibers and stronger contractions necessitate precise, deeper injections. Beard growth complicates placement, requiring angled needle approaches. Under-dosing leaves residual lines, while over-dosing risks stiffness.
Microdroplet Technique Targets Fine Lines Without Total Paralysis
Tiny, diluted injections soften wrinkles while retaining partial muscle function. This method suits patients fearing a “plastic” look. Strategic placement along the hairline avoids heaviness in the brow area. Results appear natural but may require touch-ups sooner.
Botox Prevents Static Wrinkles When Used Proactively
Early intervention in the late 20s or 30s stops repetitive motions from etching lines into the skin. Studies show 40% fewer deep wrinkles after five years of use. Pairing with sunscreen enhances long-term skin texture.
Alcohol Increases Bruising Risk by Thinning Blood Pre-Injection
Consuming alcohol 24 hours prior enlarges blood vessels, raising bruise likelihood. Supplements like fish oil and vitamin E have similar effects. Arnica cream post-treatment reduces discoloration. Cannula needles minimize vessel damage in prone patients.
Post-Injection Exercise Speeds Toxin Breakdown via Blood Flow
Intense workouts within 6 hours disperse Botox unevenly, reducing efficacy. Patients avoid hot yoga, running, or weightlifting for 24 hours. Facial massages and saunas also accelerate metabolic clearance.
Chronic Migraine Patients Experience Fewer Headaches Post-Treatment
Botox relaxes muscle tension linked to occipital nerve irritation, cutting migraine frequency by 50% in some cases. Effects overlap with cosmetic benefits, lasting 10–12 weeks. Insurance rarely covers this dual-purpose use.
Immune Resistance Renders Botox Ineffective in Rare Cases
1–3% of users develop antibodies against the toxin’s protein structure. Switching to Xeomin—a “naked” neurotoxin without additives—often restores efficacy. Lower doses and longer intervals between sessions reduce immune recognition.
Smokers Retain Botox Effects Longer Due to Slower Metabolism
Nicotine constricts blood vessels, delaying toxin breakdown in muscles. Smokers may see results persist for 4–5 months versus 3–4 in non-smokers. However, smoking accelerates skin aging, counteracting cosmetic benefits.
Asymmetrical Injections Correct Uneven Brow Elevation
A skilled injector administers 1–2 extra units on the weaker side to balance hooded brows. Real-time adjustments during forehead animation ensure symmetry. Pre-treatment photos track progress and refine future dosing.
Brows Can Lift Subtly With Strategic Lower-Forehead Dosing
Weakening the frontalis muscle’s downward pull allows natural elevators to lift the brows. Overdoing this risks a “Spock eyebrow” appearance. Conservative dosing achieves a 1–2 mm lift, ideal for tired-looking eyes.
Hyaluronidase Reverses Over-Paralysis in 24–48 Hours
This enzyme breaks down misplaced Botox, resolving eyelid ptosis or frozen muscles. Rarely needed, it’s a safety net for inexperienced injectors. Recovery takes 3–7 days, depending on overdose severity.
Genetic Collagen Variants Affect Long-Term Wrinkle Depth
Patients with COL3A1 mutations develop deeper lines despite Botox, due to weaker skin support. Combining treatments with hyaluronic acid fillers compensates for collagen deficits. Genetic testing guides personalized regimens.
Botox Weakens Muscle Memory for Expression-Related Wrinkles
Repeated treatments train muscles to contract less forcefully over time. Some patients extend intervals between sessions after 2–3 years. Maintenance requires 20–30% fewer units annually.
Postmenopausal Hormonal Shifts Reduce Botox Efficacy
Declining estrogen thins skin, making wrinkles more pronounced despite muscle relaxation. Combining Botox with topical estrogen creams improves skin thickness and elasticity. Results vary by individual hormone levels.
Neurotoxin Diffusion Risks Increase Near Thin Eyelid Skin
Shallow injections around the orbital rim allow toxin migration into levator muscles. Using higher concentrations and smaller volumes minimizes spread. Cold compresses post-injection reduce swelling and diffusion.
Forehead Botox Alters Hairstyle Choices Temporarily
Patients with heavy bangs or fringes may adjust styles if brow heaviness occurs. Muscle relaxation settles in 2 weeks, after which styling returns to normal.
Stress-Induced Jaw Clenching Worsens Forehead Wrinkles
Bruxism strains temporalis muscles, indirectly tightening the frontalis. Combining forehead and jawline Botox reduces overall tension. Effects on wrinkles last 30% longer in high-stress patients.
Allergic Reactions Are Rare but Require Immediate Care
Hives, swelling, or breathing issues post-injection signal allergy to Botox’s albumin stabilizer. Epinephrine and antihistamines manage symptoms. Switching to albumin-free neurotoxins like Jeuveau prevents